The Rise of AI Agents - A Comprehensive Guide
The Rise of AI Agents: A Comprehensive Guide
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how we work, play, and communicate—and at the forefront of this revolution are AI agents. These autonomous systems are changing the way complex tasks are executed across industries, from optimizing business operations to coding assistance in software development. In this guide, we explore what AI agents are, how they function, their benefits, and best practices for using them.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous software systems capable of performing tasks, making decisions, and interacting with environments independently. They combine the power of advanced algorithms, machine learning, and large language models (LLMs) to learn from data, adapt over time, and execute actions that were once the sole domain of human decision-makers.
Unlike traditional AI models that simply respond based on pre-trained data, AI agents can:
Autonomously plan and execute tasks Interact with external tools and databases Continuously learn from past experiences Provide more accurate, personalized responses This ability to act independently makes them highly effective in dynamic and complex environments.
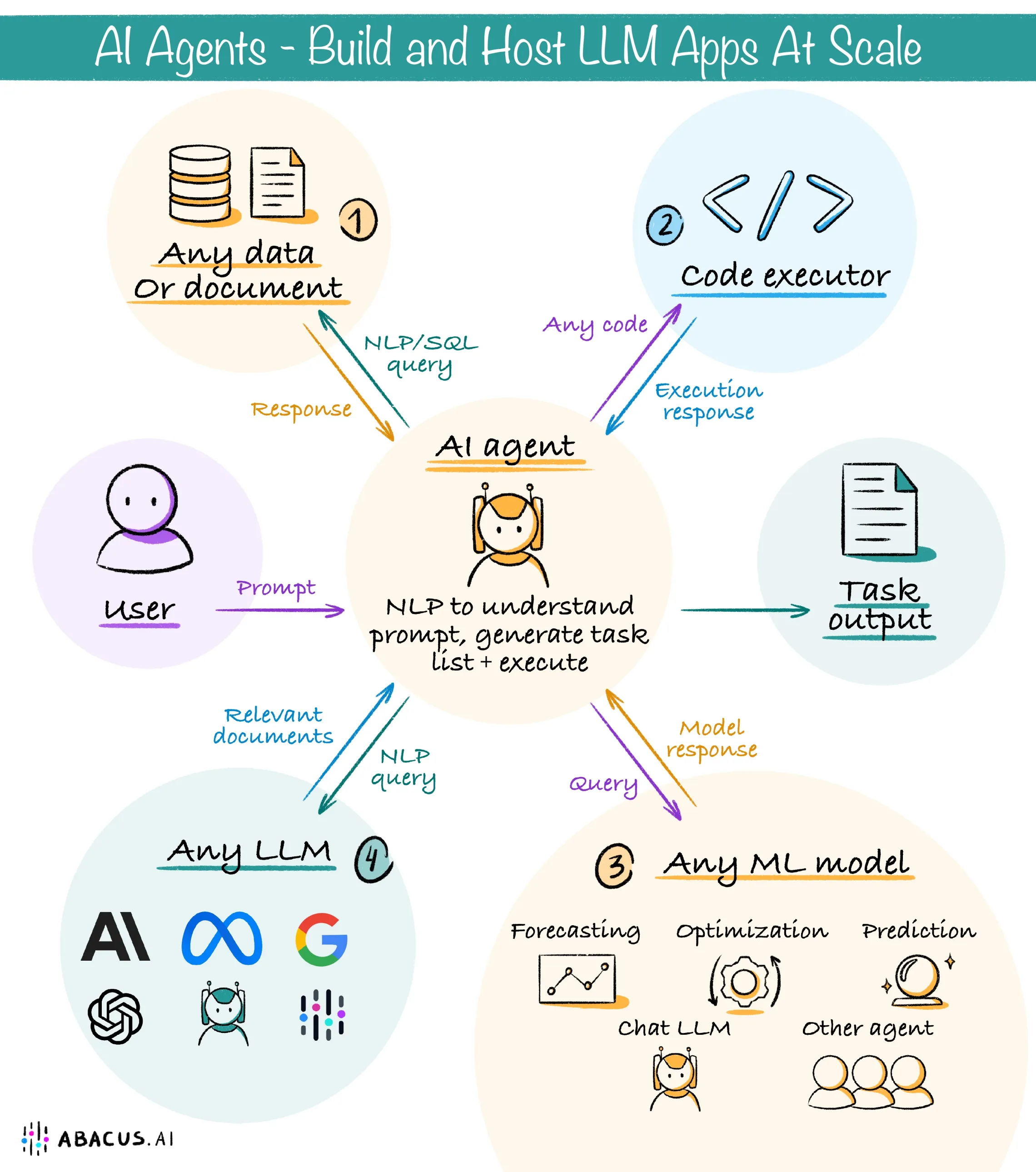
How AI Agents Work
AI agents operate through a series of well-defined steps that include goal setting, planning, reasoning, and learning. Here’s a closer look at their operational framework:
1. Goal Initialization and Planning
Every AI agent begins its journey by receiving a task or goal—typically defined by a developer or user. The agent then:
Breaks down complex tasks into manageable subtasks: This planning phase ensures the task is addressed methodically. Incorporates predefined rules and parameters: These guidelines ensure that the agent follows expected pathways while still leaving room for autonomous decision-making.
2. Reasoning with Tools and Data
Once a goal is set, the AI agent analyzes the current context and utilizes available tools to:
Gather necessary information: Whether the data comes from APIs, web searches, or internal databases, the agent fills any knowledge gaps. Continuously update its internal model: As new data is obtained, the agent revises its approach and self-corrects its actions. Engage in step-by-step reasoning: By breaking down a task into iterative “think-act-observe” cycles, AI agents deliver informed decisions.
3. Learning, Feedback, and Adaptation
Modern AI agents improve over time by leveraging feedback mechanisms:
Storing interaction history: The agent remembers past decisions and their outcomes, which helps refine future actions. Employing human-in-the-loop (HITL) strategies: Occasional human oversight ensures that learning is aligned with user expectations and maintains quality. Iterative refinement: Continuous self-assessment minimizes errors and optimizes performance.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents come in various forms. Their complexity can range from simple rule-based systems to sophisticated learning entities. The most common types include:
#Simple Reflex Agents Operate solely on the current state of the environment with preprogrammed rules. Example: A thermostat that triggers heating based on set conditions.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Leverage both current perceptions and historical data to predict future states. Example: A smart vacuum that maps a room to avoid obstacles.
Goal-Based Agents
Define specific end-goals and plan sequences of actions accordingly. Example: A navigation system that calculates the fastest route.
Utility-Based Agents
Optimize tasks based on a utility function that measures the “benefit” of each action. Example: A routing assistant that chooses the best travel path considering time, cost, and traffic.
Learning Agents
Continuously refine their performance by learning from new experiences, feedback, and iterative adjustments. Example: Personalized recommendation systems that adapt based on user behavior.
AI Agents in Action: Use Cases Across Industries
AI agents are already making their mark in several fields, offering tangible improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. Here are a few standout examples:
Software Development
Automated Code Reviews and Testing: AI agents can automatically review code, detect vulnerabilities, and suggest improvements, significantly reducing manual effort. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): By automating routine tasks, AI agents speed up the development cycle, enabling rapid iteration and deployment. AI-Powered Coding Assistants: Tools such as GitHub Copilot harness AI to assist in code generation, debugging, and optimization, leading to higher-quality software and enhanced productivity.
Healthcare
Patient Treatment Planning: AI agents analyze vast datasets to assist in diagnostics and tailor individualized treatment plans. Medical Data Analysis: They streamline routine tasks like data entry and analysis, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
Finance and Supply Chain
Real-Time Data Analysis: AI agents predict market trends, optimize supply chains, and enhance fraud detection, ensuring organizations remain agile in a rapidly changing environment. Automated Transaction Processing: With minimal human intervention, AI agents manage routine financial processes and maintain system security.
Customer Experience
Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: AI agents engage with customers in real time, providing personalized support and reducing wait times. Feedback Loop Integration: Constantly evolving via user feedback, these agents offer solutions that are increasingly tailored and precise.
Best Practices for Implementing AI Agents
To harness the full potential of AI agents while mitigating risks, consider the following best practices:
Maintain Detailed Activity Logs: Transparency is key. Logging every action taken by an AI agent builds trust and makes troubleshooting easier. Ensure Interruption Capabilities: Always allow for human intervention, especially when an AI agent is engaged in critical operations. This safeguards against unintended infinite loops or errors. Assign Unique Agent Identifiers: Unique IDs help trace and audit agent activities, which is particularly useful in multi-agent frameworks. Keep Humans in the Loop: While AI agents are designed for autonomy, human oversight helps ensure decisions align with business objectives and ethical guidelines. Prioritize Data Privacy and Security: Robust security measures must be in place to protect sensitive data processed by AI agents. Scale and Flexibility: Design agents with scalability in mind so they can grow with your organization’s evolving needs.
The Future of AI Agents
As technology evolves, the capabilities of AI agents will continue to expand. Some anticipated trends include:
Enhanced Collaboration: Future agent systems will feature more sophisticated multi-agent frameworks, where agents work in concert to deliver even more robust solutions. Improved Decision-Making: Advances in machine learning and real-time data integration will further refine the accuracy of AI agent decisions. Broader Industry Adoption: From healthcare and finance to education and transportation, AI agents are poised to become integral components in a variety of sectors. Greater Emphasis on Explainability: As AI agents become more autonomous, clear and transparent decision-making will be increasingly important to build user trust and meet regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
AI agents are not just a futuristic concept—they are here, and they are reshaping the way we work across industries. By combining goal-oriented planning, sophisticated reasoning, and adaptive learning, AI agents stand at the forefront of automation and innovation. Whether you’re a developer looking to streamline your code review process or a business aiming to enhance customer interactions, understanding and leveraging AI agents can unlock significant advantages.
Embrace the future today by exploring the possibilities of AI agents and transforming your workflows with intelligent automation.
Stay ahead of the curve by subscribing to our newsletter for the latest insights and trends in AI technology.
This article was inspired by the insights from Google Cloud, IBM, and GitHub, providing a well-rounded look at the revolution of AI agents and their immense potential in today’s digital landscape.
Tags: ai techonology guide automation
